Project Settings
There are some options which can be configured for the Rapier library that change the physics simulation for the whole project. These can be accessed from Project Settings -> Physics -> Rapier:
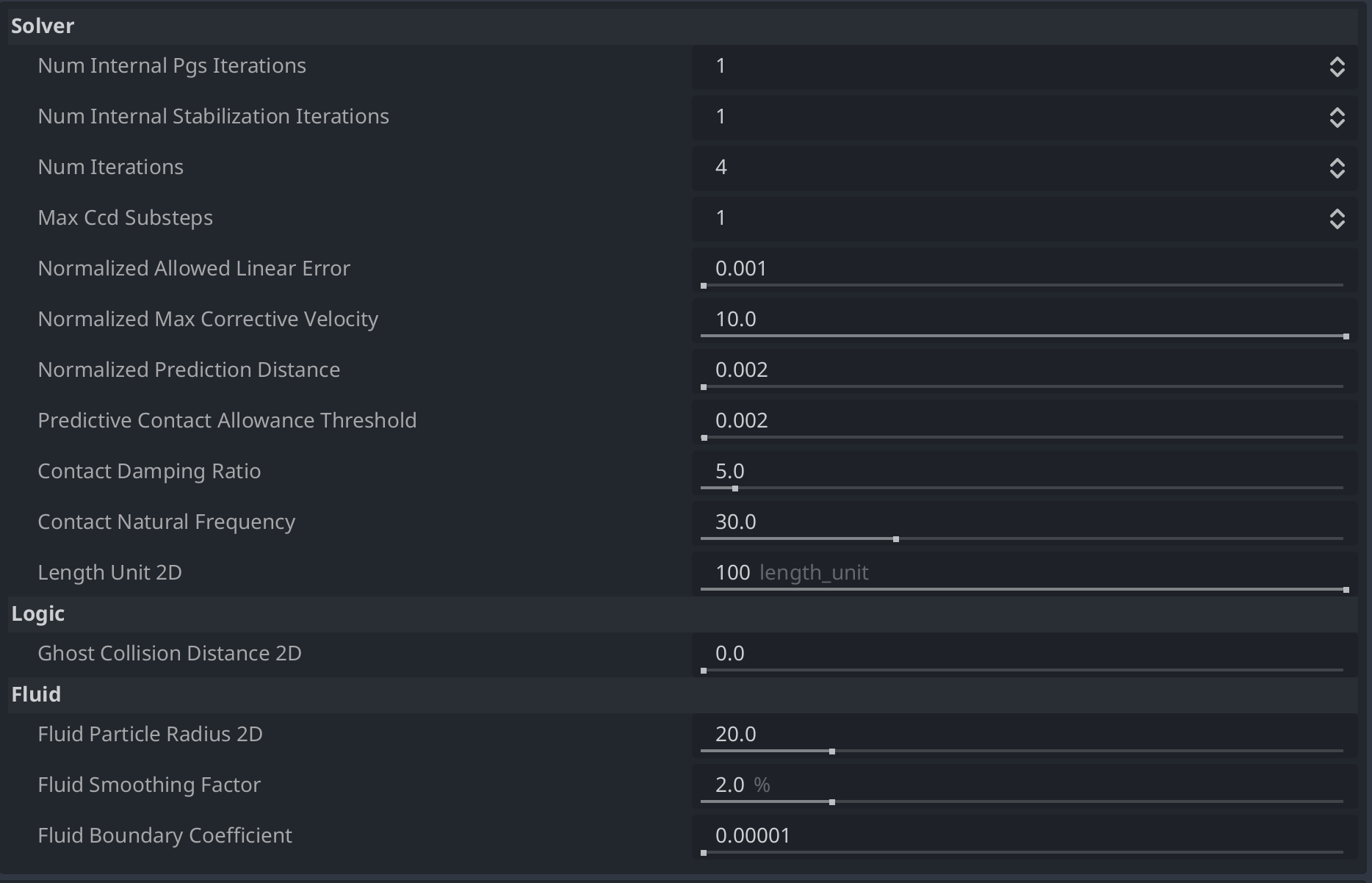
There are also 2 presets available, one for Performance and one for Stability. They both set some settings that improve one or the other.
Solver
-
Num Internal Pgs Iterations: Number of internal Project Gauss Seidel (PGS) iterations run at each solver iteration (default: 1).
-
Num Internal Stabilization Iterations: The number of stabilization iterations run at each solver iterations (default: 1).
-
Num Iterations: The number of solver iterations run by the constraints solver for calculating forces (default: 4). Higher values produce more accurate and stable simulations at the cost of performance.
- 4 (default): Good balance for most games
- 8-12: Use for demanding scenarios (stacks of objects, complex machinery)
- 1-2: Use if performance is critical and accuracy can be sacrificed
-
Max Ccd Sub Steps: Maximum number of substeps performed by the solver (default: 1).
-
Normalized Allowed Linear Error: Amount of penetration the engine won’t attempt to correct (default: 0.001). This value is implicitly scaled by length_unit.
-
Normalized Max Corrective Velocity: Maximum amount of penetration the solver will attempt to resolve in one timestep (default: 10.0). This value is implicitly scaled by length_unit.
-
Normalized Prediction Distance: The maximal distance separating two objects that will generate predictive contacts (default: 0.002). This value is implicitly scaled by length_unit.
-
Predictive Contact Allowance Threshold: Any given "contact point" may actually be a predictive point-- these points do not actually represent a contact for this frame. (default: 0.002) These false contacts are pruned out by up to the given threshold. This value is implicitly scaled by length_unit.
-
Contact Damping Ratio: > 0: The damping ratio used by the springs for contact constraint stabilization. Larger values make the constraints more compliant (allowing more visible penetrations before stabilization). (default 5.0).
-
Contact Natural Frequency: > 0: the natural frequency used by the springs for contact constraint regularization.
Increasing this value will make it so that penetrations get fixed more quickly at the expense of potential jitter effects due to overshooting. In order to make the simulation look stiffer, it is recommended to increase the contact_damping_ratio instead of this value. (default: 30.0).
-
Length Unit 2D: The approximate size of most dynamic objects in the scene. For 2D 100 pixels equal to 1 meter, as gravity in Godot is 980, and in real life it is 9.8. (default 100)
-
Length Unit 3D: The approximate size of most dynamic objects in the scene. For 3D 1 pixel is equal to 1 meter, as gravity in Godot is 9.8, and in real life it is 9.8. (default 1)
Logic
- Ghost Collision Distance 2D: The algorithm that prunes ghost contacts is applied only for contacts below this distance. (default 0.15)
Fluid
- Fluid Particle Radius: The Particle Radius used for each Particle when simulating Fluids. (default 2D = 20.0 and 3D = 0.5)
- Fluid Smoothing Factor: The Smoothing Factor used when simulating Fluids. (default 2.0)
- Fluid Boundary Coefficient: The coefficient that is multiplied with the force that liquids apply to boundaries before they are applied. Generally fluids have very high density (eg. 1000), and in Godot object have mass of 1 as default, as such this coefficient is a way to translate between the two. Without this, the fluid throws objects around at very high speeds. (default 0.00001)